UV Light: Discovery and Visibility, Subtypes, Artificial sources & Examples
4.5 (141) · € 5.00 · En stock
UV light is also known as ultraviolet light is a sort of electromagnetic radiation, which is usually invisible to the human eye. Its wavelength ranges from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz).

Ultraviolet radiation, Definition, Examples, Effects, Wavelengths, Types, & Facts

Sources and measurement of ultraviolet radiation - ScienceDirect
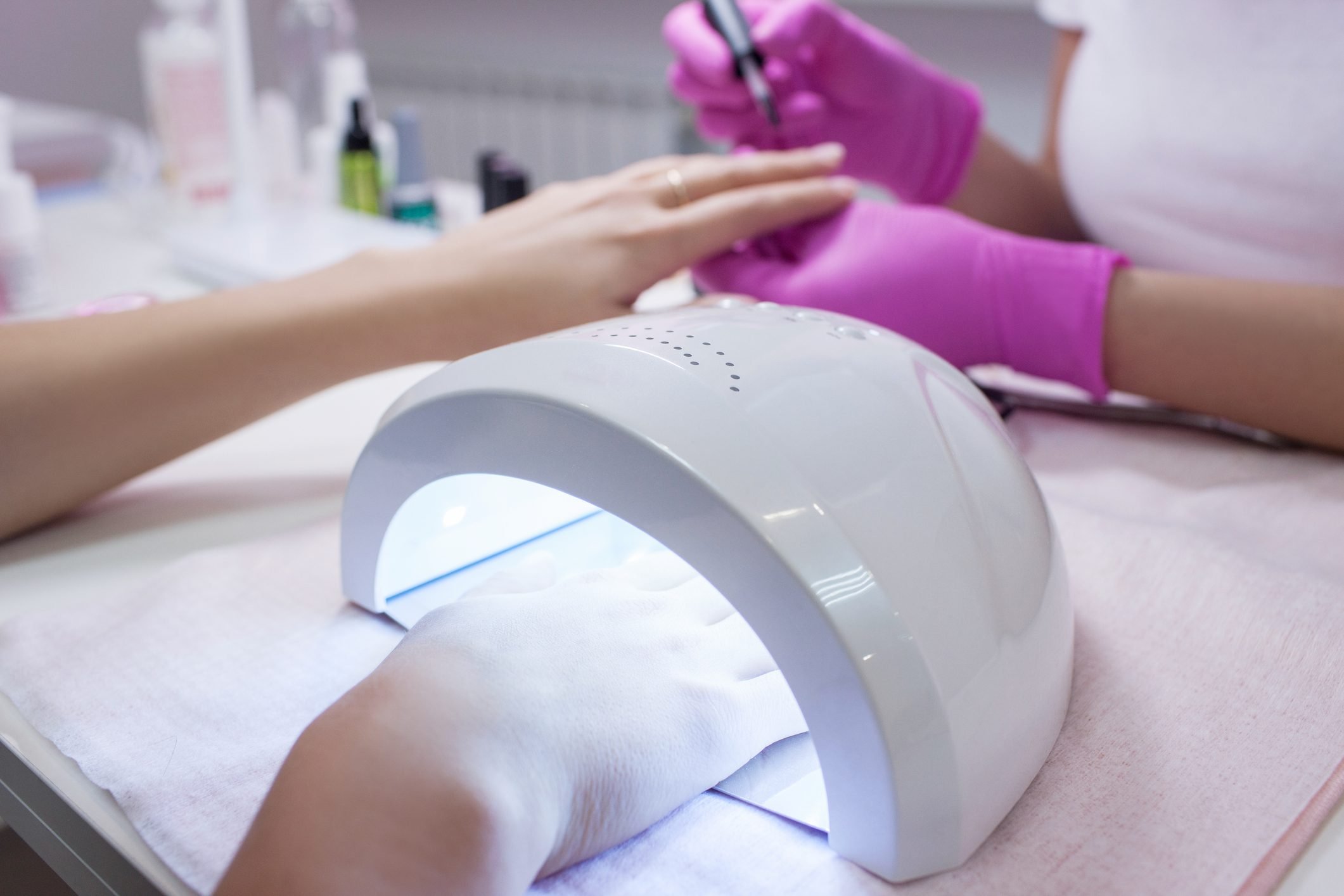
8 Sources of UV Light Damage You're Ignoring
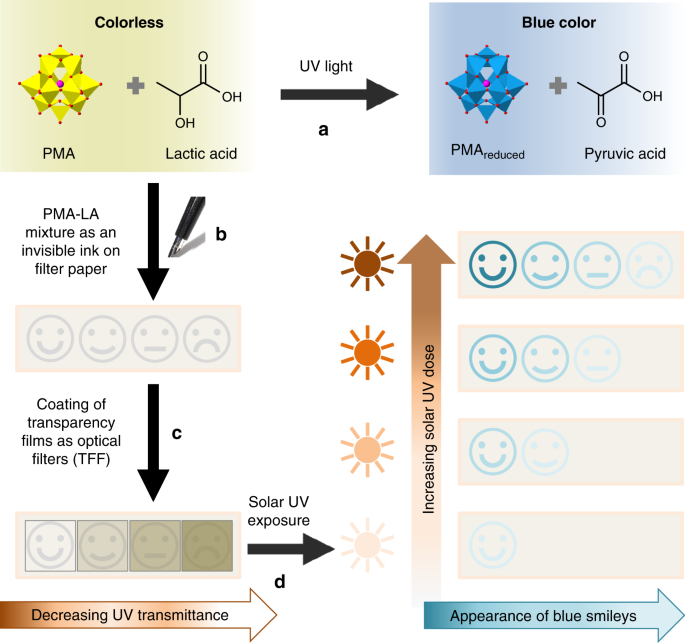
Skin color-specific and spectrally-selective naked-eye dosimetry of UVA, B and C radiations

What Is Ultraviolet Light (UV Light)? - Definition, Types, Effects, Video, and FAQs

Ultraviolet radiation, Definition, Examples, Effects, Wavelengths, Types, & Facts
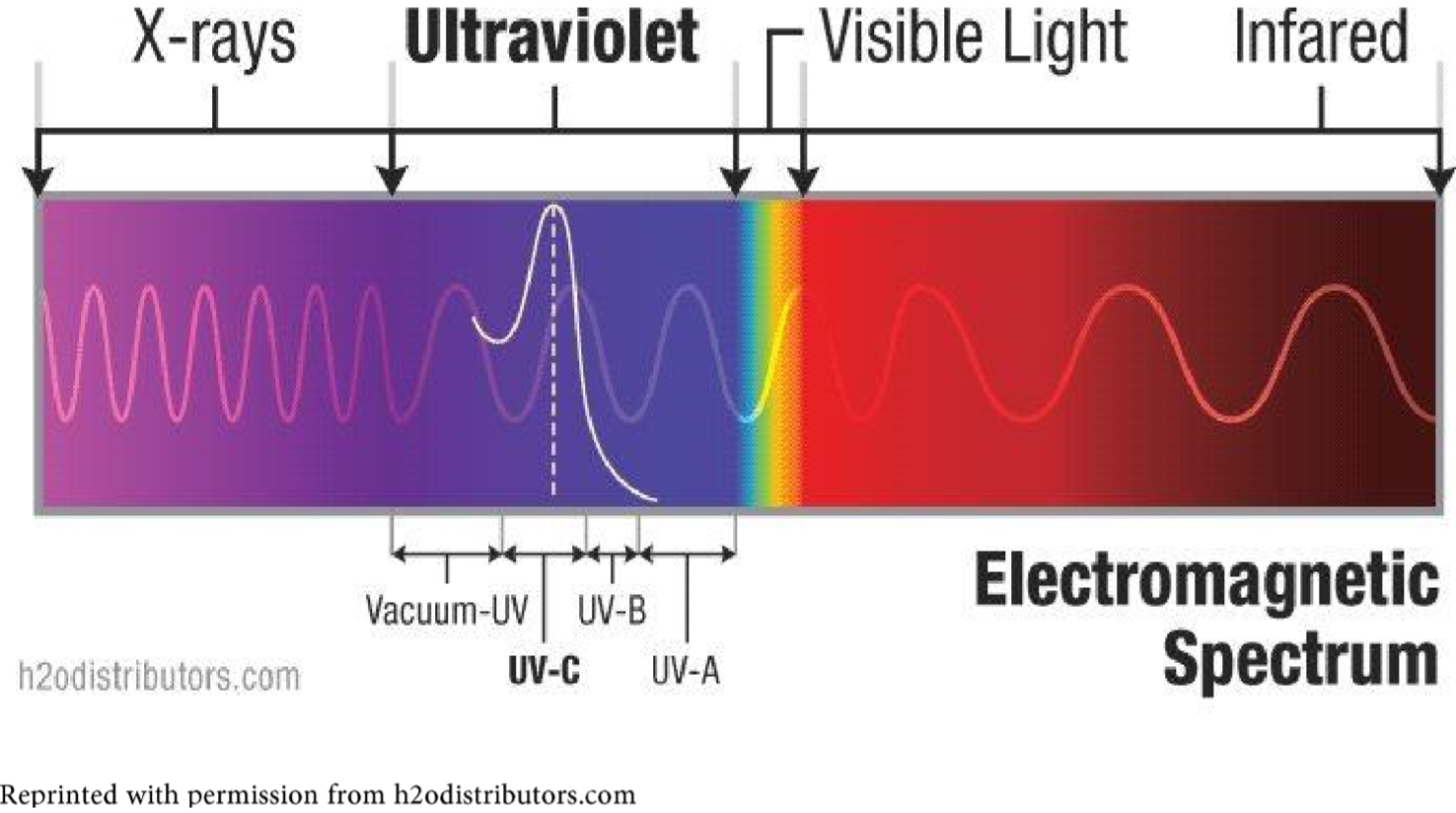
4: Detection and Absorption of Ultraviolet Light (Experiment) - Chemistry LibreTexts

UVA Radiation, DNA Damage, and Melanoma

A) Spectral reflectance of stimuli (1=100%). (B) Spectral

NIR-Activated Spatiotemporally Controllable Nanoagent for Achieving Synergistic Gene-Chemo-Photothermal Therapy in Tumor Ablation

Ultraviolet - Wikipedia

Sources and measurement of ultraviolet radiation - ScienceDirect

Recent Applications and Future Perspectives of Chemiluminescent and Bioluminescent Imaging Technologies

Controlled tumor heterogeneity in a co-culture system by 3D bio-printed tumor-on-chip model












