Human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet
5 (552) · € 5.50 · En stock
A study led by an NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre scientist has identified, for the first time, how the human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR). Dr Nathan Hawkshaw is the lead author of a research paper published in Clinical & Translational Immunology, an open access, peer-reviewed journal.

Human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet radiation

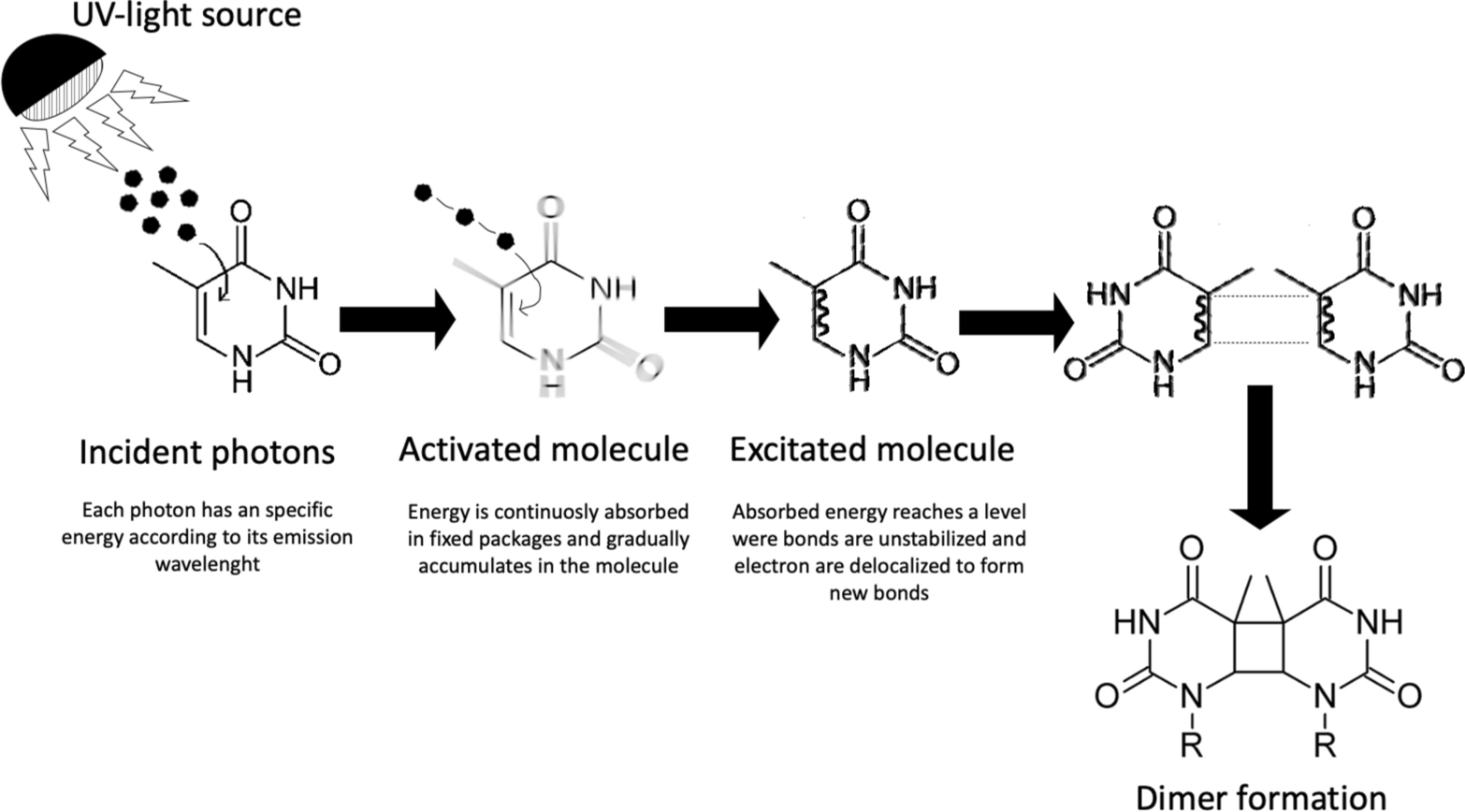
Photoaging: UV radiation-induced inflammation and immunosuppression accelerate the aging process in the skin

Topical application of glycolic acid suppresses the UVB induced IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1 and COX-2 inflammation by modulating NF-κB signaling pathway in keratinocytes and mice skin - ScienceDirect

4‐phenylpyridine suppresses UVB‐induced skin inflammation by targeting c‐Src in vitro and in vivo - Kim - 2022 - Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine - Wiley Online Library
Quercetin suppresses MMP-1 and COX-2 expression and blocks collagen

Naringenin Inhibits UVB Irradiation-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Skin of Hairless Mice

Solar UV radiation reduces the barrier function of human skin
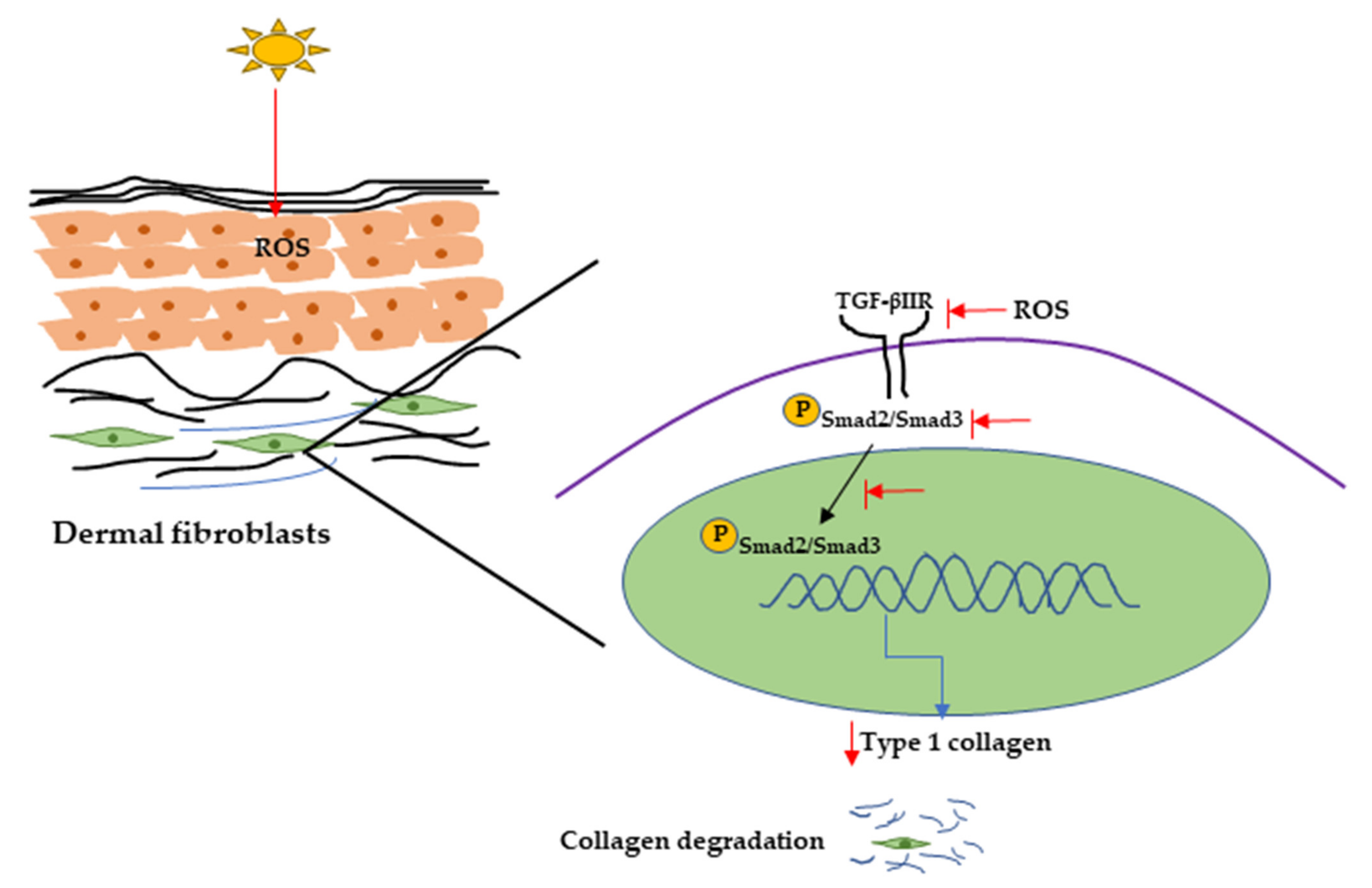
Protective effects of galangin against H2O2/UVB-induced dermal fibroblast collagen degradation via hsa-microRNA-4535-mediated TGFβ/Smad signaling

Food-seeking behavior is triggered by skin ultraviolet exposure in males

Human Novel MicroRNA Seq-915_x4024 in Keratinocytes Contributes to Skin Regeneration by Suppressing Scar Formation: Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids

4‐phenylpyridine suppresses UVB‐induced skin inflammation by targeting c‐Src in vitro and in vivo - Kim - 2022 - Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine - Wiley Online Library
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Systemic immune by UV radiation. Exposing the skin to UV radiation

Particulate matter-induced skin inflammation is suppressed by polyphenol-enriched dietary supplement via inhibition of the AhR/ARNT signaling pathway - ScienceDirect